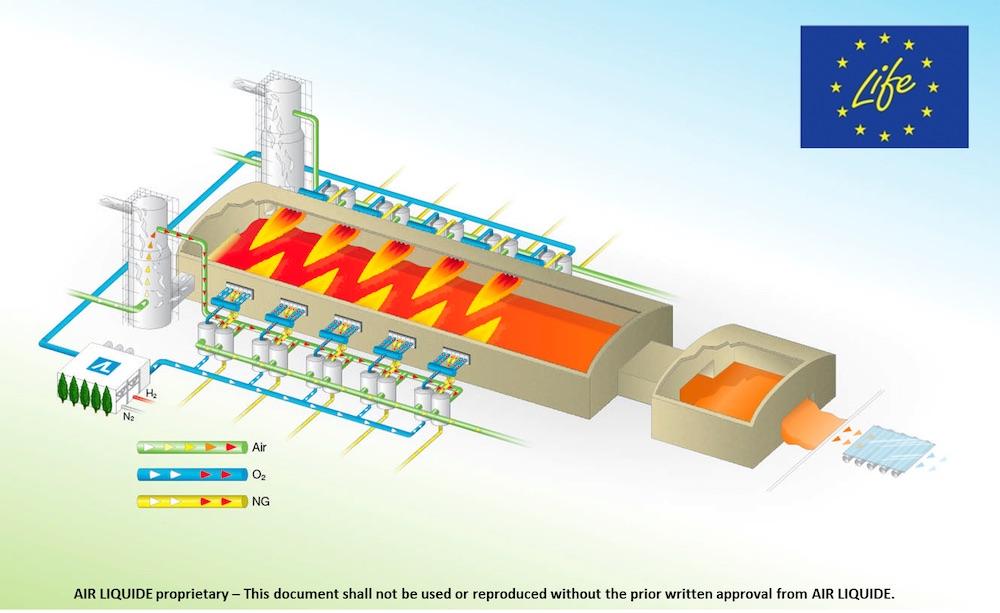
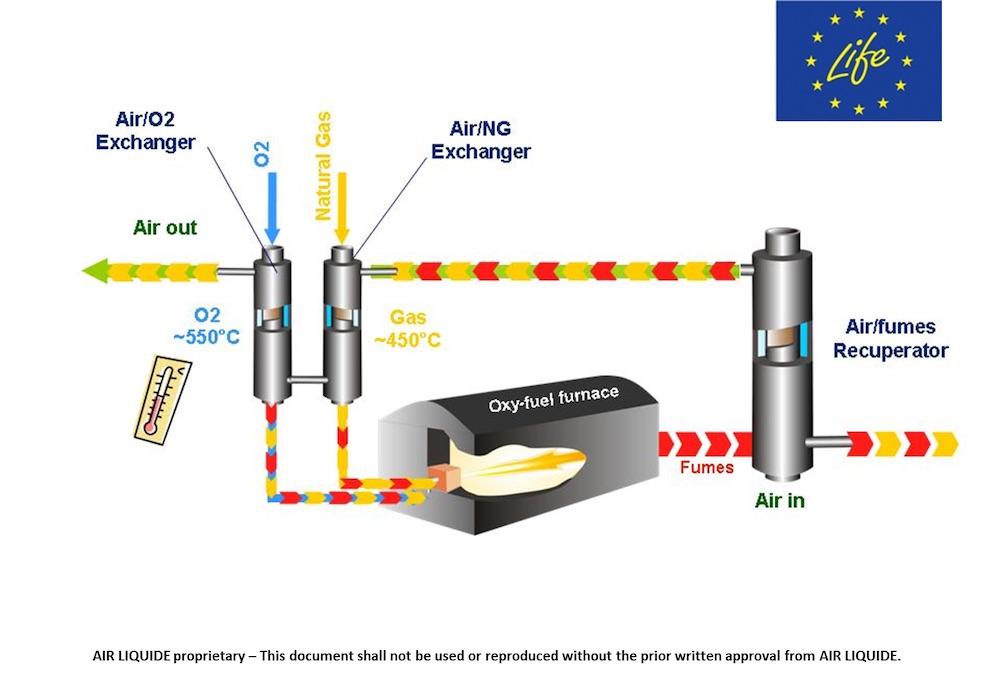
Hot Oxycombustion furnace design
Melting activities are a very energy intensive part of the glass production process, and make up for most of AGC Glass Europe’s energy consumption and atmospheric emissions. AGC continuously optimises and improves its production processes from an environmental point of view. In its quest to reduce environmental impact, AGC stepped up to develop an innovative oxygen combustion technology for float production.
Traditional float glass furnaces use air as oxidant. Air contains around 21% oxygen and 79% nitrogen. The nitrogen is useless for the combustion process and produces nitrogen oxides (NOx) at high temperature. Thus using pure oxygen instead of air would reduce the energy needed for combustion (no longer needing to heat the nitrogen) and also prevent the formation of NOx. Accordingly, AGC Glass Europe began research into flat glass furnaces using 100% oxygen as an oxidiser, instead of air. Developing new techniques for glass furnaces is a complicated and long term project. There were many issues to overcome: the use of oxy-combustion was rare in the flat glass industry as its economic profitability was low. It also presented numerous technical challenges. New technologies can affect the lifetime of the furnace or the quality of the glass. Also a glass furnace runs 24/7 and cannot be stopped and cooled down during its lifetime (15-18 years). Most technologies can therefore only be installed during a furnace rebuild.
After years of research, multiple studies, intense collaboration at R&D level, industrial level and with an external partner Air Liquide, AGC Glass Europe started up a furnace working with pure oxygen instead of air. What’s more, AGC overcame the profitability issue by developing a system that reuses heat from waste gases to preheat oxygen and natural gas before it is injected into the furnace, which yields additional significant energy savings. The Hot-Oxycombustion furnace was born!
The furnace located in Boussois (France), producing architectural clear glass, was the first float furnace in Europe to operate fully on oxycombustion and proved to be the most ecological float furnace in the world. A few years later, AGC started a second furnace using that same technology at Retenice plant (Czech Republic), producing mainly automotive glass. This second industrial application confirmed the potential of this new technology for producing high quality automotive colour glass, which has higher quality requirements than architectural glass.
Sustainability highlight
AGC Glass Europe started up its first hot oxycombustion furnace in Boussois (France). This furnace proved to be the most ecological float furnace in the world. After three years of employing the method at full scale in Boussois, the plant’s furnace emission targets have been met and even exceeded: CO2, NOx and SOx, emissions were reduced by 15%, 83% and 34.5% respectively. Furthermore, the plant’s furnace consumed 25% less energy.
More on hot-oxycombustion furnace design and energy-efficient production technologies on agc-glass.eu/sustainability
Innovation highlight
As an alternative to the usual float glass furnace design using air as oxidant, AGC Glass Europe has developed a furnace working with pure oxygen instead of air. In addition AGC developed a unique heat recovery system to preheat the natural gas and oxygen before it is injected into the furnace. The furnace located in Boussois (France), producing architectural clear glass, was the first float furnace in Europe to operate fully on oxycombustion and the first in the world to have the natural gas and oxygen preheated. It was developed in partnership with Air Liquide. A second furnace using that same technology started at Retenice plant (Czech Republic), producing mainly automotive colour glass.
This project has been funded in part by
"European Commission Environment-LIFE Programme"
with reference LIFE07 ENV/F/179 and LIFE11 ENV/CZ/000488
More information on the project and its results are available at: http://www.oxyfuel-heatrecovery.com/ (France)
and http://www.agc-hoxygas.eu/ (Czech Republic).
Schematical views of the process: courtesy of Air Liquide