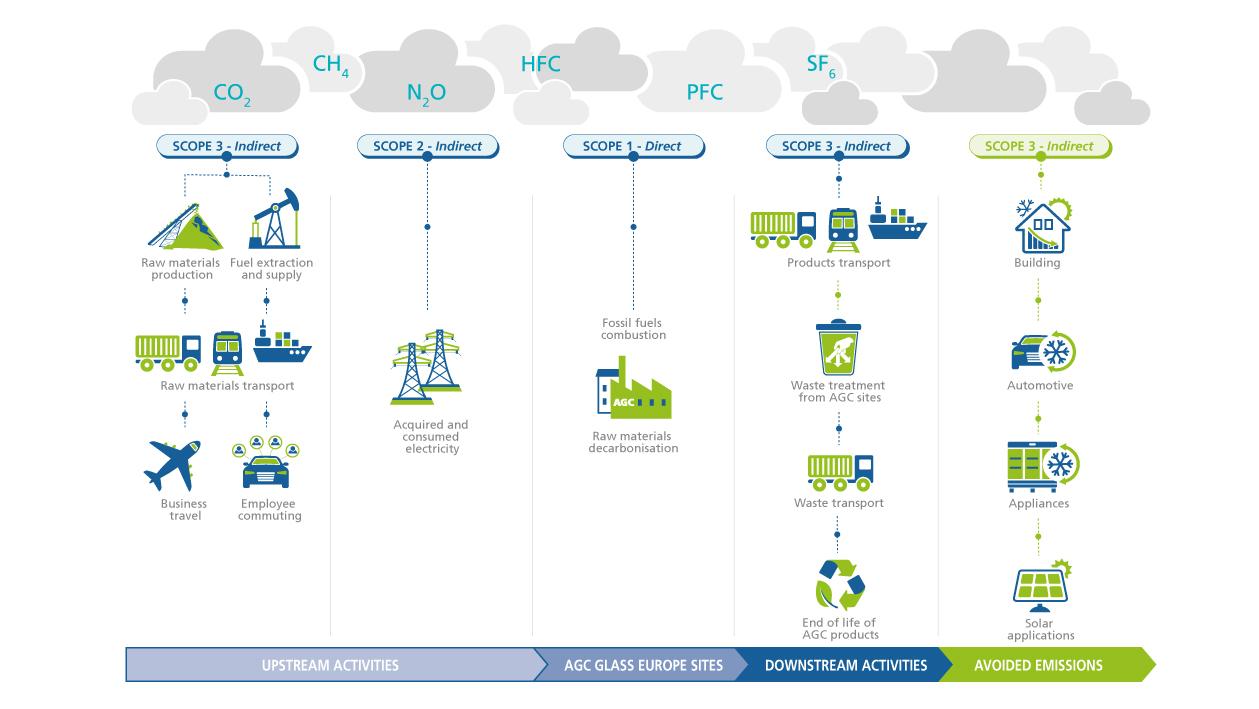
- Building: AGC has developed a full range of high-performance double and triple glazing, for use both in residential and in commercial buildings. Depending on the product and the geographical region these glazings help to keep the heat inside (i.e. reducing the need for heating) or to keep it outside (i.e. reducing the need for cooling). Both heating and cooling consume energy (and thus lead to CO2 emissions), thus, reducing these needs makes it possible to avoid CO2 emissions. Additionally, glass being transparent, it allows daylight to enter the building and consequently reduces the need for artificial lighting
- Automotive: AGC has developed IRIS coating, a special coating for windshields that keeps out much of the solar heat, thus reducing the need for air conditioning. This saving in air conditioning means a consequent saving in fuel, so further avoiding CO2 emissions.
- Appliances: thanks to its specific coatings, AGC is one of the leaders on the market for glass for doors of commercial refrigeration appliances: chilled display cabinets and freezers that are common in supermarkets for sale of dairy products, produce, food and beverages. Fitting glass doors to these appliances allows the products to be displayed clearly while saving large quantities of energy.
- Solar applications: AGC produces building-integrated photovoltaic glass, solar mirrors etc. Our glass is used to generate “green” electricity, thus, reducing the consumption of standard electricity (generated from fossil fuels).
Once every five years, AGC Glass Europe also assesses these avoided emissions to get a global picture of our impact. Indeed, energy efficient products are often more sophisticated and generate higher impacts at production stage compared to standard products. Considering the sole production stage is missing the key stage of the product life cycle: the use stage.
Avoided emissions are emission reductions that occur outside of a product’s life cycle or value chain, but as a result of the use of that product(1) . Other terms used to describe avoided emissions include climate positive, net-positive accounting, and scope 4. For the purposes of calculating energy savings provided by the glazing on buildings and hence the avoided CO2 emissions, several methodologies were followed such as: The "GHG Protocol for Project Accounting, ISO 14064-2 Greenhouse gases -- Part 2: Specification with guidance at the project level for quantification, monitoring and reporting of greenhouse gas emission reductions or removal enhancements" and "METI Guidelines for Quantifying GHG emission reductions of goods or services through Global Value Chain".
The main principle is to consider next to the production impacts from one calendar year, the benefits from the products manufactured during this year over their full life cycle, compared to a baseline scenario. E.g. in case of glazings for building the avoided emissions are calculated as the savings between advanced low-e coatings compared to clear double glazing or single glazing over a 30 years lifetime.
The calculation was carried out using the whole building energy simulation software Energy Plus (Developed by the US Department of Energy). This software realises a dynamic simulation with adjustable time step, based on external temperature, solar irradiance and wind effect. It takes into accounts for external and internal loads, HVAC settings, and lighting requirements.
(1) Estimating and reporting the comparative emissions impacts of products by S Russell. World Resources Institute, Working paper, 2019.
To integrate the effect of local climates, Europe has been divided into seven climate zones based on the climate in representative cities:
- North – Helsinki
- East – Moscow
- Central – Prague
- Central Continental – Frankfurt
- Central Maritime – Brussels
- South – Rome
- South Central – Sofia
For overseas markets, several locations outside Europe were chosen as references:
- Middle East & Maghreb - Dubai
- Sub-Saharan Africa - Johannesburg
- South-Eastern Asia - Singapore
- North America - New York
- Latin America - Buenos Aires
- Oceania - Auckland
- Japan – Tokyo
Taking into account the heating/cooling energy needed per climate zone according to climate data, the kWh/m².year saved by renovation or construction of new buildings to higher standards, the average lifetime of buildings in Europe and the relevant emission factors, it is possible to calculate the tonnes of CO2 avoided thanks to our Insulating Glass products.
For all the products manufactured by AGC Glass Europe in 2020, we calculated that the amount of CO2 avoided for heating and cooling was around 24,800,000 tonnes.
Additionally, about 8,700,000 tonnes of CO2 are also avoided thanks to the benefit of daylight allowed through the glazings, totalling altogether around 33,530,000 tonnes of CO2.
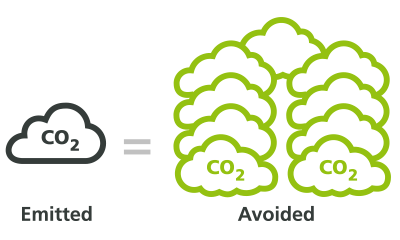
Calculating both CO2 emissions and CO2 avoided leads to a final result of 1:9 (i.e. 3,535,000 tonnes of CO2 vs. 33,530,000 tonnes – reference year 2020), meaning that for each tonne of CO2 emitted by AGC Europe activities, more than 9 tonnes of CO2 are avoided thanks to the use of our products!
This of course is a very encouraging result, showing that even a “heavy” industry such as ours can have large overall benefits for society!